Experiencing server connection issues? Follow these targeted steps to diagnose and resolve common problems immediately:
1. Verify Basic Network Connectivity
Problem: No connection to the network or server is unreachable.
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure Ethernet cables are securely plugged in (both ends). If using Wi-Fi, confirm you are connected to the correct network and signal is strong.
- Restart Hardware: Power cycle your modem/router and your local machine.
- Ping the Server: Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS/Linux). Type ping server_ip_address_or_hostname. If you receive replies, basic connectivity exists. If not, investigate your network settings or DNS.
2. Validate Login Credentials & Permissions
Problem: "Access Denied", "Login Failed", or "Invalid Credentials" errors.

- Double-Check Credentials: Ensure username and password are entered correctly, noting case sensitivity.
- Verify Permissions: Confirm your user account has the necessary privileges to access the server/service. Contact your server administrator if unsure.
- Password Reset: If possible, reset your password through the authorized method.
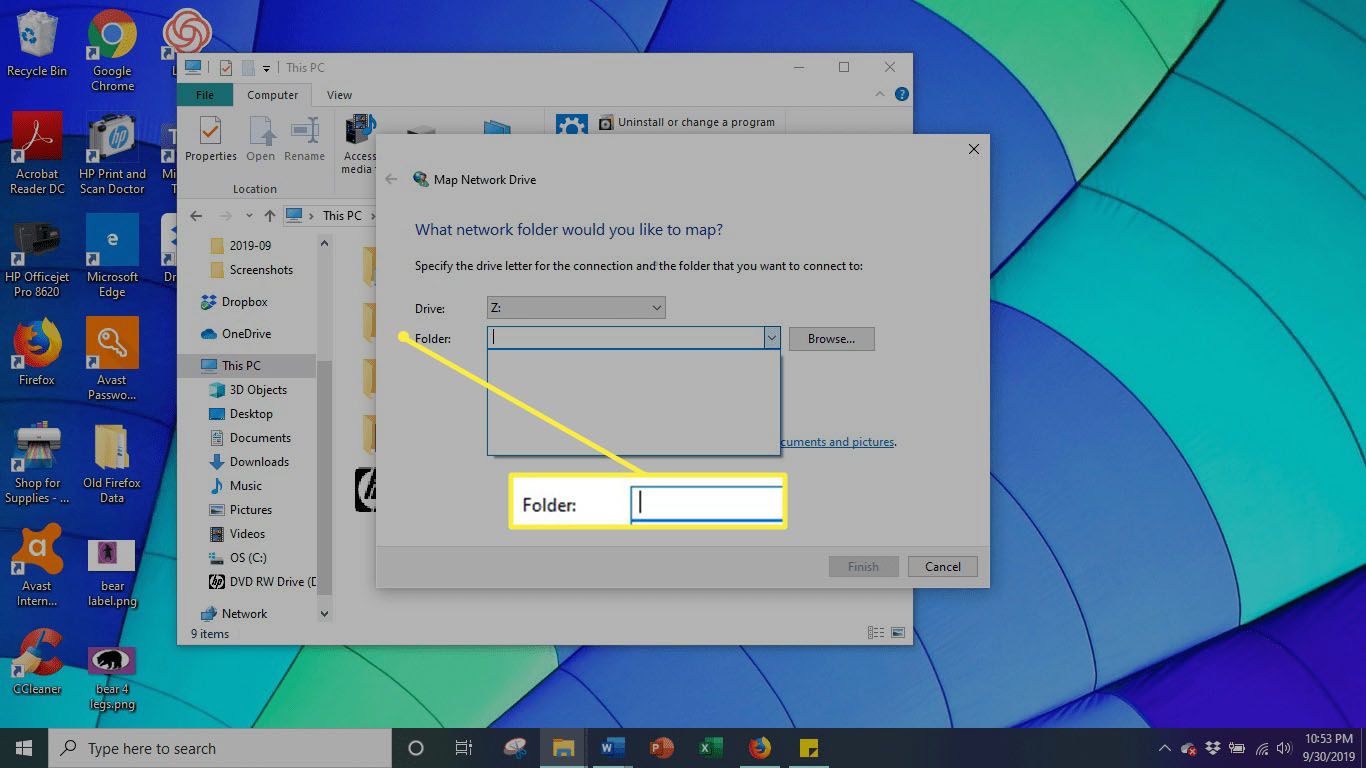
3. Confirm Server Address & Port
Problem: Unable to locate the server.
- Verify IP/Hostname: Ensure you are using the correct IP address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the server.
- Specify Correct Port: The target service (SSH, RDP, HTTP, FTP, database) runs on a specific port (e.g., 22, 3389, 80, 443, 21, 3306). Verify you are connecting to the right port. Append it to the address like server_ip:port if required by your client.
4. Check Firewall & Security Settings
Problem: Connection attempts are blocked.
- Local Firewall: Temporarily disable your local machine's firewall (Windows Defender Firewall, macOS Firewall, third-party security suites) to test if it's the culprit. If successful, re-enable and create an inbound/outbound rule for the specific application/port.
- Server Firewall: The server's firewall must allow traffic on the required port. This requires server admin access to configure rules (e.g., via iptables, firewalld, or cloud console security groups).
5. Assess Service Status & Resources
Problem: Server appears unreachable or unresponsive.
- Service Running: Ensure the specific service you're connecting to (e.g., SSH daemon, web server, database service) is actually running on the server. Admin access is needed to check (sudo systemctl status servicename on Linux).
- Server Resources: The server might be overloaded (high CPU, RAM, disk usage) or completely unresponsive (crashed). Check server monitoring dashboards if available, or ask the administrator.
6. Inspect DNS Resolution
Problem: Connecting via hostname fails, but IP address works.
- Flush DNS Cache: On your local machine:
- Windows: Open Command Prompt as admin, run ipconfig /flushdns.
- macOS/Linux: Use sudo dscacheutil -flushcache or sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches.
- Check DNS Settings: Verify your machine is using the correct DNS servers (e.g., your router, company DNS, public DNS like 8.8.8.8).
Systematic Isolation: Test these fixes in sequence. Start with local checks (your connection, credentials, client settings), then progress to network and server-side issues. Documenting results helps pinpoint the root cause.