The slmgr command, part of Windows Software Licensing Management Tool, provides powerful CLI options for managing activation. Employing it correctly ensures reliable and compliant system activation.
Understanding slmgr Basics
Execute commands in elevated Command Prompt for full privileges. Use * to perform tasks like installation, activation, and status verification. Always verify system compatibility with the Windows version.
Core slmgr Activation Commands
- slmgr /ipk [ProductKey]: Installs a product key; ensure it's valid and genuine.
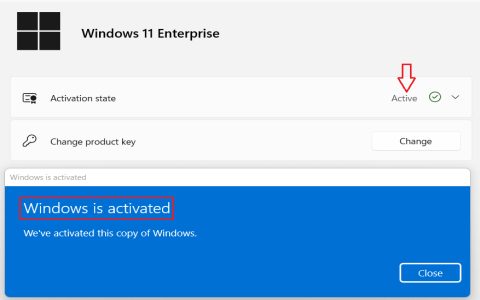
- slmgr /ato: Attempts online activation after key installation; confirm internet connectivity.
- slmgr /dli: Displays license information for quick validation.
- slmgr /dlv: Shows detailed activation status including expiry and errors.
Best Practices for Reliable Activation
- Run commands as administrator to avoid permission issues and ensure full execution.
- Verify key legitimacy before use to prevent activation failures and maintain compliance.
- Backup current activation state with slmgr /dti before major changes for easy recovery.
- Activate in test environments first to catch errors without impacting production systems.
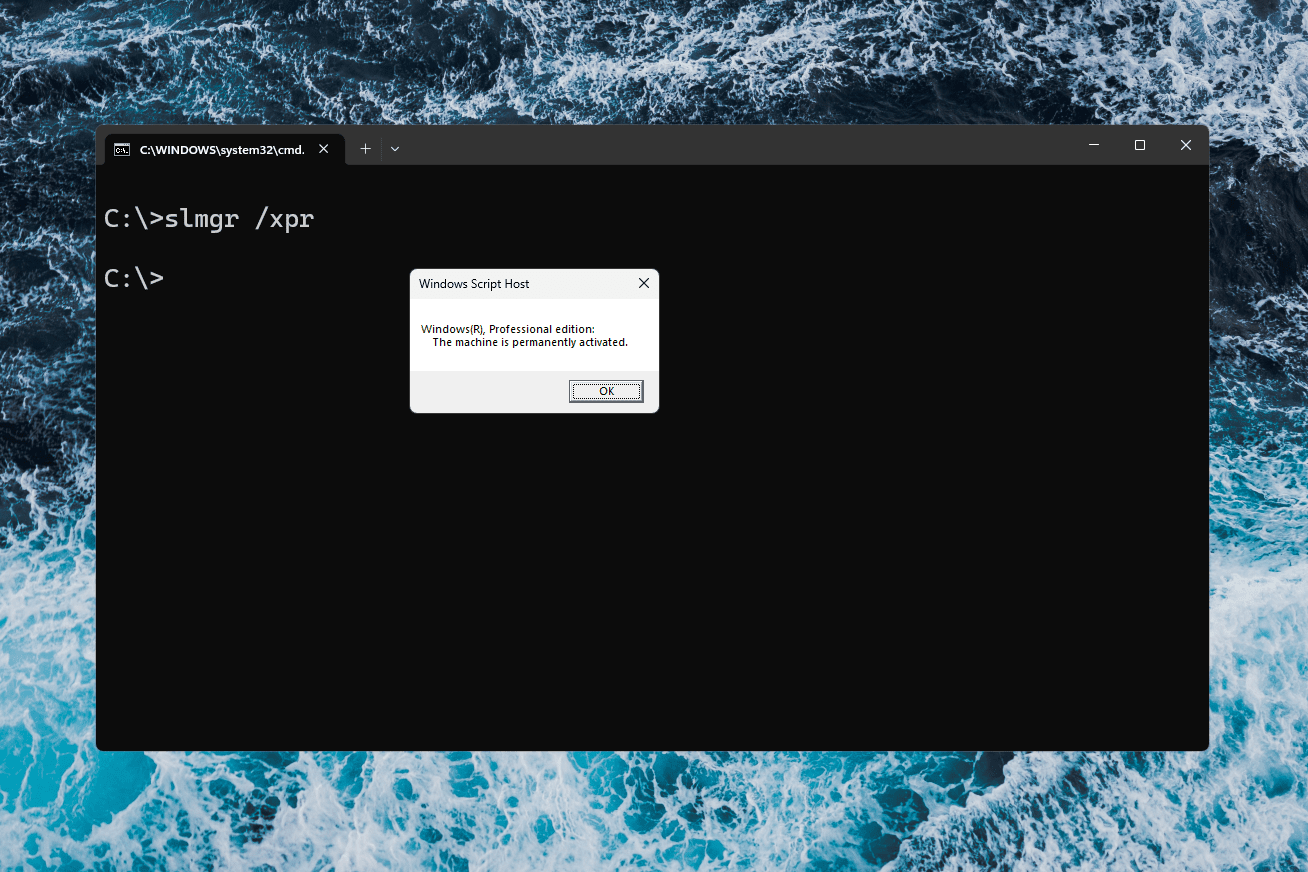
- Monitor license renewal dates using slmgr /xpr to avoid unexpected expirations.
- Combine with KMS servers for enterprise setups by including /skms parameter if applicable.
Troubleshooting Common Scenarios
For activation errors like 0xC004F074, re-enter the key and re-attempt /ato. If slmgr hangs, restart the service via command prompts. Always cross-check logs in Event Viewer for deeper diagnostics.