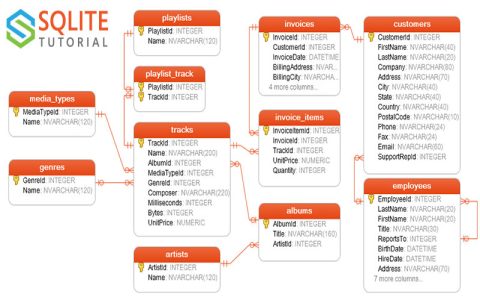
A .db file is a database file used to store structured data in tables. It's commonly associated with SQLite, a lightweight, embedded database engine. Here's how they work and how to use them:
How .db Files Work (Concept)
- Self-Contained: The entire database – structure (tables, views) and data – is stored in a single cross-platform file.
- Serverless: Doesn't require a separate server process (like MySQL or PostgreSQL). Programs access the file directly using a library (e.g., SQLite library).
- Structured Storage: Data is organized into tables with defined columns (name, data type).
- SQL Support: Data is accessed and manipulated primarily using Structured Query Language (SQL) commands.
- File Format: The .db file has an internal binary format optimized for efficient reading/writing by the SQLite engine. It includes a header, schema definitions, and data pages.
Basic Steps for Beginners
1. Get a Database Browser:
- Install a visual tool like DB Browser for SQLite (free). This avoids needing to use complex command lines initially.
2. Open/Create a .db File:
- Launch DB Browser. Click 'New Database'. Choose a location, type a filename ending in
.db(e.g., '*'), and save. - To open an existing .db file: Click 'Open Database' and select the file.
3. Create a Table:
- Go to the 'Database Structure' tab. Click 'Create Table'.
- Enter a table name (e.g., 'customers').
- Define columns. For each column, specify:
- Name (e.g., 'id', 'name', 'email').
- Type (e.g., 'INTEGER', 'TEXT', 'REAL').
- Constraints (Optional: like 'PRIMARY KEY' for 'id').
- Click 'OK'. The table schema is saved inside the .db file.
4. Add Data (Insert Rows):
- Go to the 'Browse Data' tab. Select your table.
- Click the 'New Record' icon. Enter data into each field for the new row.
- Click the 'Write Changes' icon to permanently save the data to the .db file.
5. View Data (Simple Query):
- Stay in the 'Browse Data' tab with your table selected. You will see all the rows you've entered.
- Alternatively, go to the 'Execute SQL' tab and type:
SELECT FROM customers;(Replace 'customers' with your table name). Click the play icon.
6. Modify Data (Update):
- In 'Browse Data', double-click a cell in an existing row, change the value, and then click 'Write Changes'.
- Use SQL in 'Execute SQL':
UPDATE customers SET email = 'new@*' WHERE id = 1;
7. Delete Data:
- In 'Browse Data', select a row and click the 'Delete Record' icon, then 'Write Changes'.
- Use SQL:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE id = 2;
Key Points to Remember
- Changes Need Saving: Tools often require an explicit 'Write Changes' or 'Save' step after adding/modifying data.
- Use SQL: Learning basic SQL (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE TABLE) is essential for working with .db files beyond simple browsing.
- Be Cautious: SQL commands like DELETE or DROP TABLE (removes a table) permanently remove data. Always backup important .db files.