Converting STP (STEP) files to STL format is crucial for 3D printing workflows, yet errors can halt production. Quickly resolve issues with these targeted fixes.
Common STP to STL Errors and Solutions
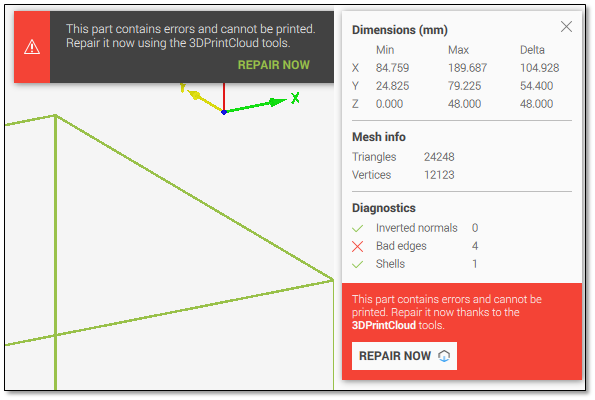
- Geometric Defects (e.g., holes or non-manifold edges): These cause STL failures. Fix by pre-checking the STP file for gaps in CAD software and repairing using "heal" tools before conversion.
- Low Resolution or Loss of Detail: Results in jagged surfaces. Adjust conversion settings to increase triangle count or use finer tessellation options to preserve details.
- File Corruption or Invalid Data: Prevents conversion. Validate the STP file for integrity by reopening it in the original CAD application and exporting a clean version.
- Unit Mismatches Causing Scaling Issues: Converts to incorrect sizes. Ensure units in both STP and STL settings match, typically set to millimeters in conversion software.
- Software-Specific Errors (e.g., import/export failures): Often tied to tool limitations. Switch to robust tools like FreeCAD or Blender for re-conversion, avoiding default options.
Pro Tips for Error-Free Conversion
Always verify STP files for errors first using CAD tools. For persistent STL flaws, manually inspect with mesh repair tools like MeshLab post-conversion to seal holes quickly.
Prevent recurring issues by standardizing units and resolution in workflows, enabling faster troubleshooting.