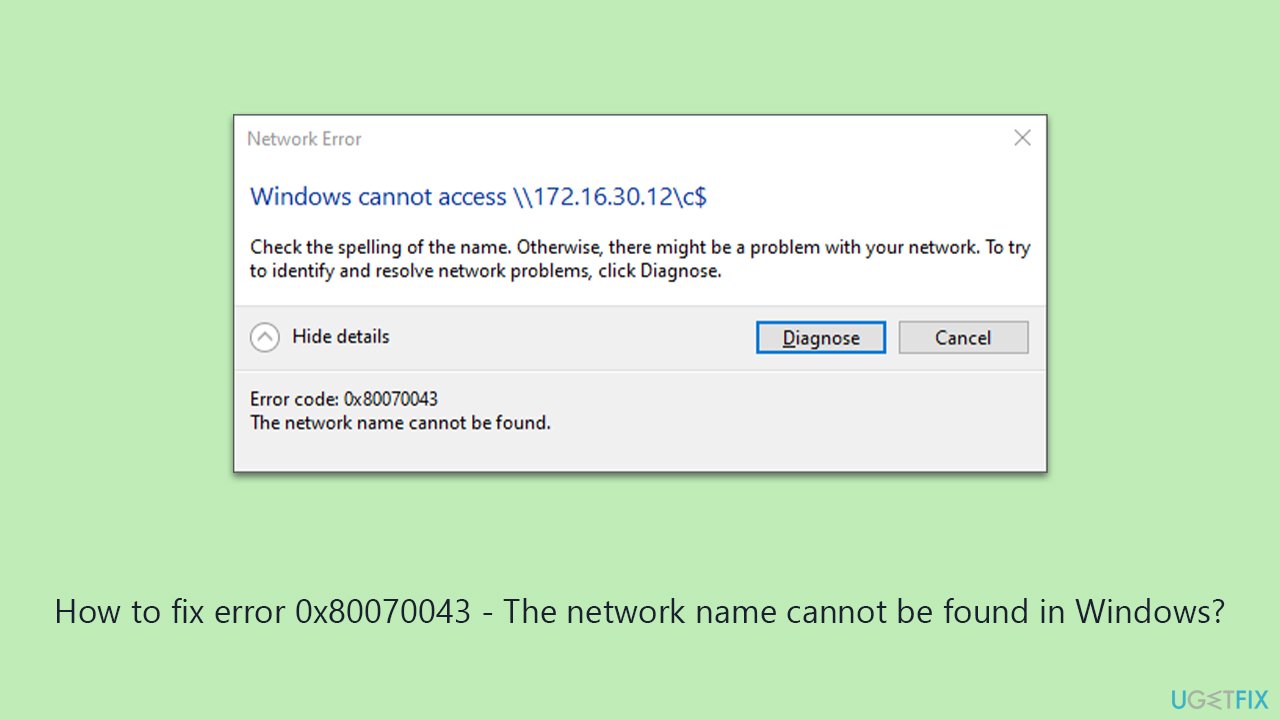
The Network Name Not Found error on Windows Server 2003 typically occurs when a client system or another server fails to resolve the target server's name to its IP address using NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) or related name resolution methods. This often stems from misconfigurations or service issues specific to legacy NetBIOS resolution. Here are the top targeted fixes:
Verify Basic Connectivity & Name Resolution
Before delving deeper, confirm fundamental network health.
- Ping the Target IP: Ensure the server itself is online and reachable (`ping <TargetServerIP>`).
- Ping the Target Name: Test name resolution (`ping <TargetServerName>`). A successful ping implies DNS resolution is working, shifting focus towards NetBIOS/WINS.
- Check Firewall Settings: Temporarily disable the Windows Firewall or other security software on the target server to rule out blocking of NetBIOS ports (UDP 137-138, TCP 139/445). Re-enable with specific rules if resolved.
Check & Restart Critical NetBIOS Services
Essential services must be running on the target server.
- Computer Browser Service: Verify its status is Started and Startup type is Automatic (Administrative Tools > Services). Restart if necessary.
- Server Service: Confirm it's Started. This is crucial for file and print sharing.
- Workstation Service: Ensure it's Started on both the client attempting the connection and the target server.
- TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper Service: Check its status is Started.
- Restart Services: After verification or changes, restart these services.
Confirm & Correct WINS and NetBIOS Settings
Accurate NetBIOS configuration is paramount.
- WINS Client Configuration: On the client experiencing the error, ensure:
- TCP/IP properties (Network Connections > NIC > Properties > TCP/IP > Advanced) have the correct WINS server IPs listed under the WINS tab.
- NetBIOS setting is Enabled or Default (preferably Enabled).
- Server NetBIOS Settings: On the target server, ensure NetBIOS is also Enabled in its TCP/IP properties > Advanced > WINS tab.
- Flush and Re-Register NetBIOS Names: On the target server, open Command Prompt:
- Stop WINS/NetBIOS: `net stop wins` (if WINS installed).
- Flush Cache: `nbtstat -R` (Note: Capital 'R').
- Re-Register: `nbtstat -RR` (Note: Capital 'R').
- Start WINS: `net start wins` (if stopped).
- WINS Replication/Consistency: If WINS is used, verify replication between WINS servers is functional and that entries for the target server are present and accurate.
Investigate LMHOSTS File
A static `LMHOSTS` file might contain outdated entries.
- Check LMHOSTS: Examine `%systemroot%system32driversetcLMHOSTS` (or `*` as a template) on the client system. Look for static entries for the target server name and ensure they are accurate and not duplicated.
- #PRE and #DOM: Verify `#PRE` and `#DOM:` tags are correctly formatted if used for preloading domain entries.
- Temporarily Rename: If suspicious entries exist, temporarily rename the LMHOSTS file to `.OLD` and retest.
DNS Configuration & Host Records
While often a NetBIOS/WINS issue, DNS problems can manifest similarly in certain contexts.
- Verify Forward/Reverse Lookup: On the client, ensure `nslookup <TargetServerName>` returns the correct IP and `nslookup <TargetServerIP>` returns the correct name.
- Check DNS Suffixes: Ensure the client's DNS suffix search list (TCP/IP properties > Advanced > DNS) includes the domain of the target server.
- Hosts File: Check the `%systemroot%system32driversetchosts` file on the client for incorrect static entries.
- DNS Record: Confirm an accurate 'A' record exists for the target server in the appropriate DNS zone.