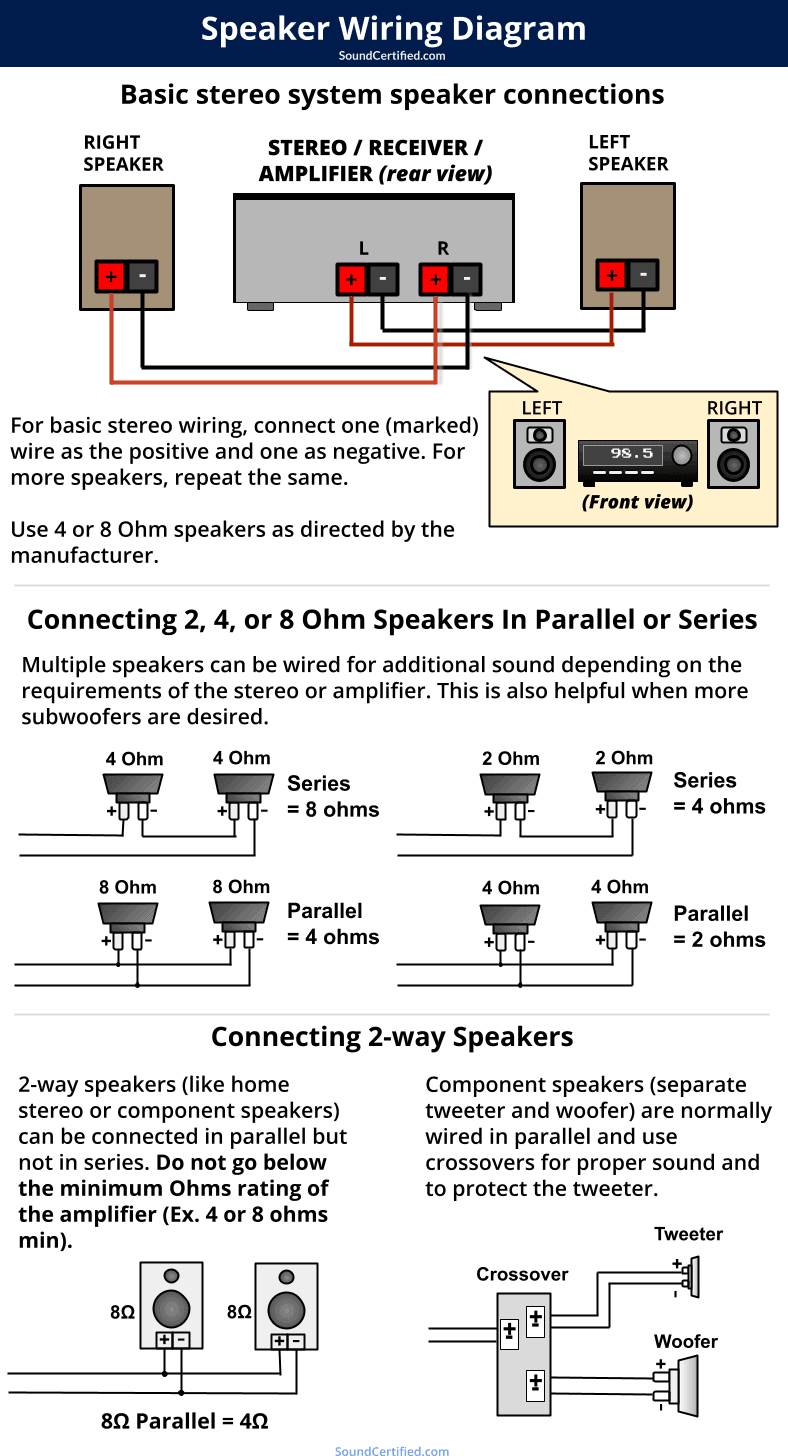
Speaker Wiring Fundamentals
Wiring speakers involves connecting them to amplifiers while matching impedance, measured in ohms (Ω). Mismatched impedance risks amplifier overload or speaker damage. Always start by checking your amplifier's minimum load rating, typically 4-8Ω.
Common Wiring Configurations
Use these methods to connect multiple speakers:
- Series Wiring: Connect positive terminal of one speaker to the negative terminal of the next. Total impedance sums (e.g., two 8Ω speakers = 16Ω). Ideal for high-impedance setups but reduces power output.
- Parallel Wiring: Connect all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together. Total impedance decreases (e.g., two 8Ω speakers = 4Ω). Increases power demand but ensures uniform volume across speakers.
Reading Wiring Diagrams
Diagrams use symbols for speakers and terminals. Identify: and marks for polarity. Straight lines represent wires; dashed lines show optional paths. Common diagrams show series/parallel hybrids to optimize impedance.
Practical Safety Tips
Power off amplifiers before wiring. Use appropriate gauge wires for distance: 16 AWG for short runs, 12 AWG for longer. Avoid loose connections; they cause heat buildup or short circuits. Always test setups at low volumes first to confirm functionality.